As technologies progress rapidly in the development of software, timely delivery of quality applications turns out to be significant. CI and CD pipelines have become tactics central to the software development approach that is now quite relevant.
They not only offer the advantage of refined development procedures but also make way for quicker and more accurate software deliveries.
In this article, we will give you a definition of CI/CD pipelines, the advantages of their use, and tips on using them.
Basic Understanding of CI/CD
Continuous Integration (CI)
Continuous Integration, or CI, is a software development tactic in which coders merge their code often, and often more than once daily. After each integration is done, the system is checked to identify integration mishaps and make corrections where necessary.
The main goal of CI is to minimize, or in other words, eliminate, integration hell, which occurs when several developers are fixing code and on mergers aiming at integrating changes that were made to a code after several days of development.
Continuous Delivery (CD)
The CD takes CI to the next level by extending the automation process right up to the staging or production environment. With the CD pipeline for each change, the automatic test is done, and it will always be in a deployable state.
Like continuous delivery but even more radical, continuous deployment deploys any change made to the code to production via an automated pipeline if the change is approved at each stage of the pipeline.
While embracing DevOps as the key to automating the software delivery process and integrating it into product development, some stakeholders may wonder why CI/CD pipelines are critical.
Faster Delivery of Features: CI/CD pipelines make a smooth and efficient release that can allow businesses to deliver features for customers faster.
Improved Code Quality: Integration testing is done automatically in order to reveal maximum bugs comfortably, and this leads to the provision of higher-quality code in the market.
Reduced Manual Work: Automation cuts the need for manpower, helps avoid mistakes, and allows developers to concentrate on adding more functionality to the product.
Enhanced Collaboration: Integrations help facilitate frequent communication between different developers and thus enhance teamwork.
Scalability: CI/CD pipelines help make it easy to scale development processes, especially with a massive and/or distributed team.
Related Blog: Finding the Right DevOps Engineer: A Comprehensive Guide
Key Components of CI/CD Pipelines You Must Know
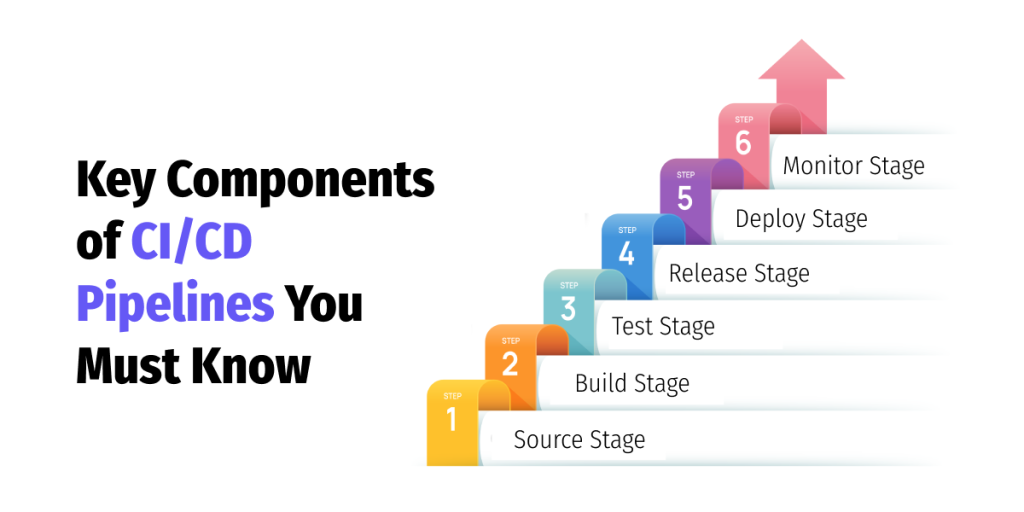

A CI/CD pipeline consists of multiple stages, each designed to validate code changes and ensure a smooth deployment process:
1. Source Stage
This is just the starting point of the CI/CD process. It is performed every time developers push their work into version control tools, such as Git.
2. Build Stage
The build stage transforms the application code into an executable form of the requirements for the release. This makes it possible to know that the code functioning is responsive and can proceed to the next level of testing.
3. Test Stage
Here, the automated tests are performed to ascertain the correctness, speed, and robustness against common risks of the included code. This may comprise unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests.
4. Release Stage
On producing the working code, the code is then compiled into a form ready to be deployed.
5. Deploy Stage
The last stage is the deploy stage; after that, the code is copied to the defined environment, for instance, staging or production. In continuous deployment, this step is completely automated from the build environment.
6. Monitor Stage
Monitoring of deployed applications is conducted to confirm that the application is working as expected. In this stage, logging, performance, and error tracking are often carried out as part of the process.
CI/CD Tools You Should Know for Your Business


There are a variety of ways to introduce CI/CD pipelines. Here are some of the most popular ones:
Jenkins: An open-source automation server with a high level of flexibility and an extensive range of plugin compatibility.
GitLab CI/CD: A component of GitLab that is used to manage the cooperation of CI/CD pipelines holistically.
CircleCI: A cloud-based CI/CD tool that is user-friendly with good speed.
Travis CI: Open-source projects widely use it because of the minimal employment of configuration files.
Azure DevOps: Combines coverage for DevOps processes, as well as CI/CD pipelines.
GitHub Actions: Enables workflow automation in and around GitHub, directly.
Setting Up a CI/CD Pipeline: Step-by-Step Guide


Step 1: Select the third platform: Version control
Choose the right tools to use in managing your codebase; there is a system, Git, for instance. Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery tools work well with sites such as GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket.
Step 2: Select a CI/CD Tool
Select a tool about your project and your team’s level of comfort with that tool. Jenkins and GitLab CI/CD are good places to begin with.
Step 3: Define Your Pipeline Configuration
Many CI/CD solutions utilize the YAML file format or templates as the main way of defining pipelines’ parameters. For example, GitLab, and GitHub Actions.
Step 4: Set Up Automated Testing
It should contain unit tests, integration tests, etc. It should contain the necessary automated testing scripts.
Step 5: Configure Deployment Stages
Define such things as staging or production. Make sure that scripts used for deployment are well set as per the various environments.
Step 6: Monitor and Optimize
For pipeline performance and application health post-deployment, then use monitoring tools for these assessments. Your pipeline should always be adjusted to be more efficient.
Standard Operating Procedures for CI/CD Pipelines
Start Small: Use a streamlined at first and slowly make it complex over time.
Automate Everything: Both code testing and deployment are among the determinants of CI/CD and should be automated.
Fail Fast: There are better ways to detect problems before they get to the point where the cost of fixing bugs is markedly high.
Enforce Code Reviews: CI/CD should be implemented together with an excellent code review strategy for the most efficient, primarily to enhance the quality of the delivered project.
Secure your pipeline: To preserve all the critical data, it is important to follow security code standards as well as incorporate security testing tools.
Use metrics: evaluate the performance of the pipeline to determine where possible changes may be of great benefit.
Challenges of Implementing CI/CD Pipelines
While CI/CD pipelines offer immense benefits, they also come with challenges:
Initial Setup Complexity: Building and construction of a pipeline can be cumbersome and requires a lot of input and expertise.
Tool Selection: Selecting the right tools that will suit the needs of the project is sometimes quite challenging.
Legacy Systems: Adopting CI/CD with legacy systems requires a certain amount of customization that is not necessary in a new environment.
Team Training: CI/CD is something that developers and operations teams should be familiar with.
Real-World Examples of CI/CD in Action
1. Netflix
The engineering team of Netflix deploys CI/CD pipelines to deploy hundreds of times daily, making streaming a perfect experience for millions of users.
2. Amazon
Amazon uses CI/CD to support the functionality of its e-commerce marketplace, minimizing the time to release new features and at the same time ensuring that the systems remain stable.
3. Facebook
Facebook also deploys numerous CI/CD pipelines to deliver chained updates of its apps and services often so that the users always get the best, unencumbered apps that are free of bugs or have slow loading speeds.
The Future Trends of CI/CD
That being the case, CI/CD pipelines will remain paramount in development practices as they go through transformative processes. Some of the advancements that today define the formation of the forthcoming new generation of pipelines are AI-driven testing, containerization using Kubernetes, and bolstered integration with DevSecOps.
Especially serverless CI/CD when pipelines exist in the cloud and do not require dedicated resources are now emerging, and teams can apply it even if they are small.
Concluding Thoughts
Continuous integration and continuous development pipelines are revolutionary to the current development life cycle since they enhance the assertion and speed of software delivery.
Hire DevOps Engineers to Optimize Your Software Development Lifecycle.
CI/CD pipelines are the basics of efficient, scalable, and reliable software development by automating monotonous work, enacting precise tests, and emphasizing collaboration.
For any modern business, whether it’s a startup or an enterprise, CI/CD is not a luxury—it’s a necessity. Deploy a small scale first, adhere to guidelines and best practices, and then build up the strengths of your pipeline over time.






